Trigonometry: (lesson 3 of 3)
Law of Cosines
The law of cosines is used:
1. to find the third side of a triangle when two sides and the included angle are given.
2. to find an angle when all 3 sides are given.
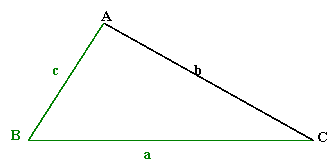
1. We are given a, c, and ∢B.
b2b=a2+c2−2accos(∢B)=a2+c2−2accos(∢B)
2. We are given sides b, c, and ∢A.
a=b2+c2−2bccos(∢A)
3. We are given sides b, a, and ∢C.
c=a2+b2−2abcos(∢C)
Example 1:
In triangle ABC, side a=8cm, c=10cm,
and the angle at B=60∘. Find side b, angle A and angle C.
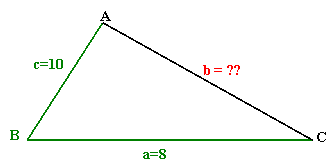
Solution:
1. Side b:
b2bbbb=a2+c2−2accos(∢B)=a2+c2−2accos(∢B)=82+102−2⋅8⋅10⋅cos(∢60∘)=164−80=84=221
2. Angle A
a28264cos(∢A)cos(∢A)cos(∢A)=b2+c2−2bccos(∢A)=102+842−2⋅10⋅84cos(∢A)=184−2084cos(∢A)=2084120=2216=213=arccos(213)≈49.1∘
3. Angle C
∢A+∢B+∢C=180∘arccos(213)+60∘+∢C=180∘∢C=120∘−arccos(sqrt213)≈120∘−49.1∘∢C≈50.9∘

