Right triangle calculator
The right triangle calculator finds the missing area, angle, leg, hypotenuse and height of a triangle. The calculator also provides steps on how to solve the most important right triangles: the 30-60-90 triangle and the 45-45-90 triangle.
Tutorial
What is right triangle?
Right triangle is a type of triangle in which the measure of one angle is 90 degrees. The side opposite the right angle is called hypotenuse. The other two sides are called legs.
Most important formulas?
This calculator uses the following formulas to find the missing elements of a right triangle.
1. Pythagorean Theorem
c2 = a2 + b2
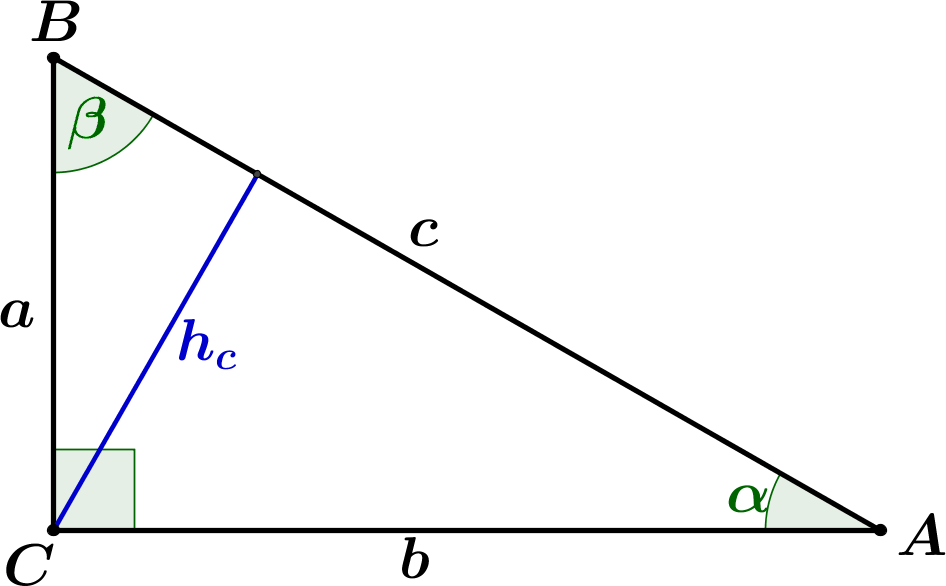
2. Area - version 1
$$ A = \frac{a b}{2} $$3. Area - verison 2
$$ A = \frac{c h_c}{2} $$4. Trigonometric functions:
$$ \begin{aligned} \sin \alpha &= \frac{a}{c}\\ \cos \alpha &= \frac{b}{c}\\ \tan \alpha &= \frac{a}{b}\\ \end{aligned} $$Solved examples
Find hypotenuse c of a right triangle if leg a = 4 cm and leg b = 8 cm.
The Pythagorean theorem is the key formula for calculating the missing sides of a right triangle. This theorem is useful when we need to find the third side if the two sides are given.
c2 = a2 + b2
c2 = 42 + 82
c2 = 16 + 64
c2 = 80
c = √80
c = √(16 · 5)
c = 4√5
Find the angle $\alpha$ of a right triangle if hypotenuse c = 14 cm and leg a = 8 cm.
To find the missing angle, we must use trigonometric functions. For this example, the sine function is appropriate as we have the hypotenuse and side a.
sin α = a / c
sin α = 8 / 14
sin α = 0.5714
α = sin-1(0.5714)
α = 39o
Special triangles
This calculator also solves special right triangles: 30-60-90 and 45-45-90
Triangle 30-60-90
Triangles with angles of 30°–60°–90° are the most common ones in high school math because they can be solved without using trigonometry. When solving this triangle, the calculator uses that the ratio of sides is 1 : √3 : 2 (see the picture below).
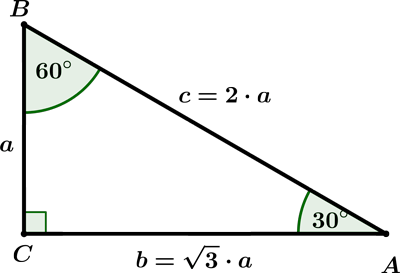
When solving a 30-60-90 right triangle, three cases can occur:
Case 1: The short leg is given.
If the short leg is a = 10, then the side b is b = a √3 = 10 √3 and hypotenuse c is c = 2 · 10 = 20.
Case 2: The long leg is given.
If the long leg is b = 12, then the leg a is a = b / √3 = 12 / √3 = 4 √3 and hypotenuse c is c = 2 · a = 8 √3.
Case 3: The hypotenuse is given.
If the hypotenuse c = 30, then the leg a is a = c / 2 = 15 and leg b is b = a √3 = 15√3.Special triangle 45-45-90
Triangle with angles of 45o – 45o – 90o is the second type of special triangle. The ratio of sides for this triangle is $ 1: 1 : \sqrt{2} $. For example, if the shortest side a = 4, then the side b is also 4 and hypotenuse c is $ c = a * \sqrt{2} = 4\sqrt{2} $.
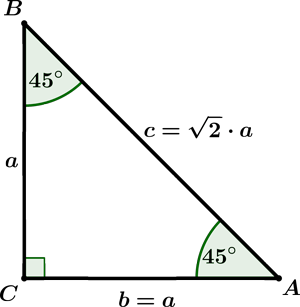
 Find two sides of a triangle ABC if leg a= $ 13\, \text{cm}$ .
Find two sides of a triangle ABC if leg a= $ 13\, \text{cm}$ .
solution
Leg $ b = 13 $
Hypotenuse $ c = 13 \sqrt{ 2 } $
explanation
Step 1: Find hypotenuse c.
From the diagram above, we can see that $ c = \sqrt{2} \cdot a $. In this example we have:
$$ c = \sqrt{2} \cdot 13 = 13 \sqrt{ 2 } $$Step 2: Find leg b.
From the diagram above, we can see that $ b = a = 13 $.
1. Right Angled Triangle definition with examples
2. Solve for a side in right triangles
3. Right triangles practice tests